Updated 9 June 2018
This article was originally published back in Jan 2018 as 'How to Show Rank Order in Queries' at Access World Forums.
Its easy to create a rank order in Access reports but not so easy in queries.
If you Bing/Google the topic you will find several methods of doing so.
The standard solution involves the uses of subqueries.
For example, see http://allenbrowne.com/ranking.html
However, the following method using the Serialize function below is, in my opinion, far easier. In addition, it is usually faster than using subqueries
CODE:
Public Function Serialize(qryname As String, KeyName As String, keyValue) As Long
On Error GoTo Err_Handler
'used to create rank order for records in a query
'add as query field
'Example Serialize("qry1","field1",[field1])
Dim rst As DAO.Recordset
Set rst = CurrentDb.OpenRecordset(qryname, dbOpenDynaset, dbReadOnly)
rst.FindFirst Application.BuildCriteria(KeyName, rst.Fields(KeyName).type, keyValue)
Serialize = Nz(rst.AbsolutePosition, -1) + 1
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
Exit_Handler:
Exit Function
Err_Handler:
MsgBox "Error " & Err.Number & " in Serialize procedure: " & Err.Description
Resume Exit_Handler
End Function
For example in this query, the function is used to create a TableID field which serves as the row number:
SELECT Serialize("qryJSONFileTables","TableName",[TableName]) AS [TableID], MSysObjects.Name AS TableName, qryJSONFileTableNames.FileID, qryJSONFileTableNames.FileNameFROM qryJSONFileTableNames INNER JOIN MSysObjects ON qryJSONFileTableNames.TableName = MSysObjects.Name
WHERE (((MSysObjects.Type)=1) AND ((MSysObjects.Flags)=0))
ORDER BY MSysObjects.Name;
Attached is a simple example database using student assessment marks for a fictitious school to further illustrate its use
It has 2 tables: tblAssessmentMarks / tblAssessmentTypes and various queries including three with rank order fields.
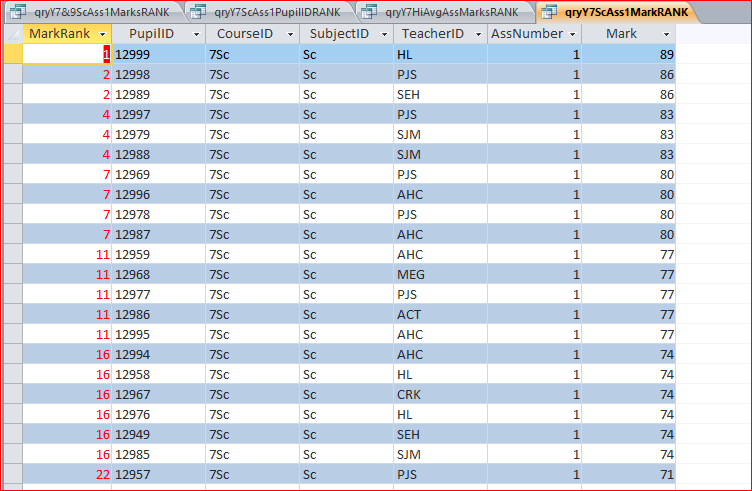
a) qryY7ScAss1MarkRANK
This sorts Year 7 Science students in rank order by mark (descending order) - as several students have the same mark, the rank values are repeated e.g. two are ranked 2 so the next is ranked 4
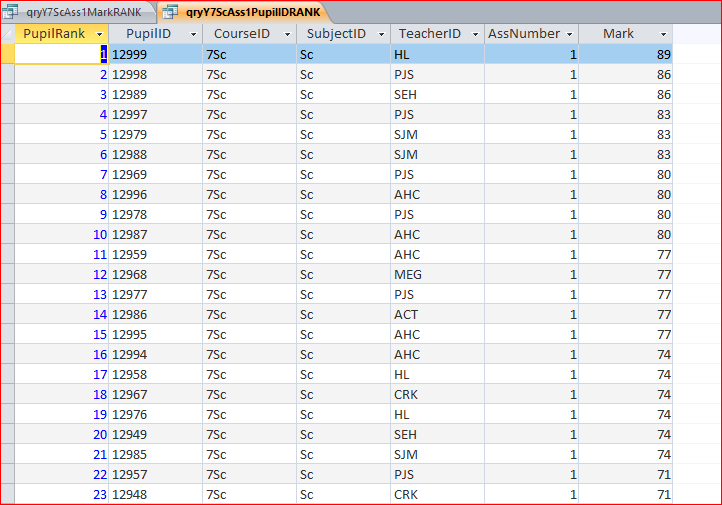
b) qryY7ScAss1PupilRANK
This is the same data but this time ranked in descending mark order by PupilID - so no repeated values for rank
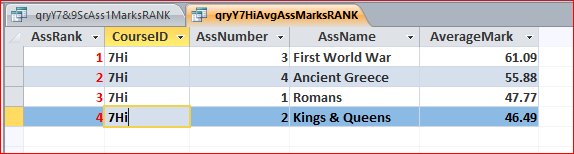
c) qryY7HiAvgAssMarksRANK
This shows Y7 History average marks by assessment in rank order
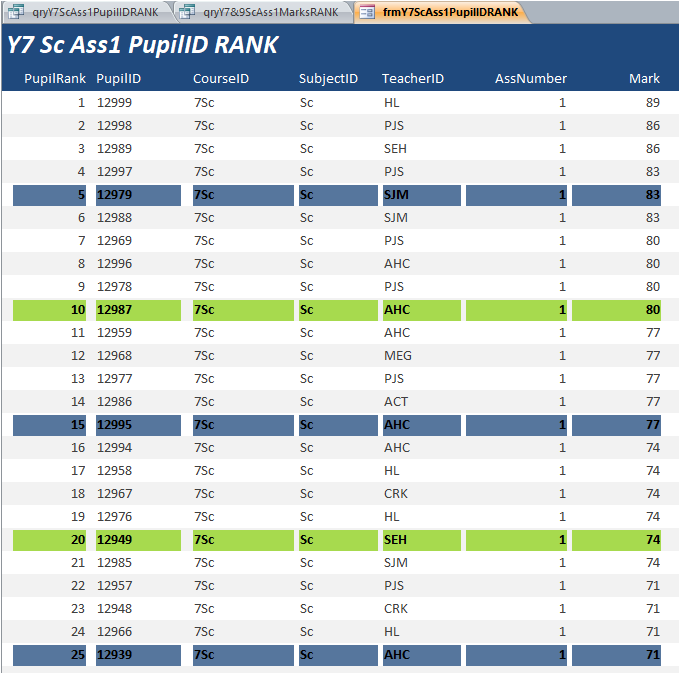
Rank order queries can also be used as record sources for forms (or reports).
Conditional formatting can also be used to assist understanding.
In the example form shown below, rank values ending in 5 are coloured blue and those ending in 0 are coloured green.
Click to download: AssessmentRankQueries.zip (Approx 0.85MB zipped)
Colin Riddington Mendip Data Systems Last Updated 9 June 2018
