Updated 12 Sept 2018
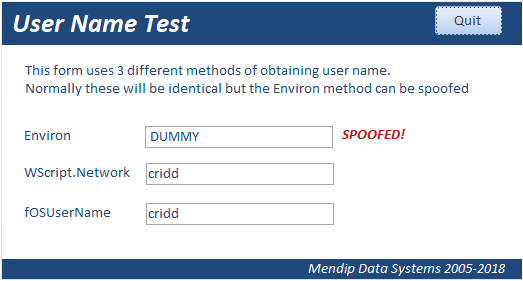
There are 3 common methods of getting the current user name in Access
1. Environ("UserName")
2. CreateObject("WScript.Network").UserName
3. fOSUserName function by Dev Ashish
As this includes API declarations, it needs to be adapted for 32-bit/64-bit systems using
conditional compilation
CODE:
#If VBA7 Then
Public Declare PtrSafe Function apiGetUserName Lib "advapi32.dll" Alias _
"GetUserNameA" (ByVal lpBuffer As String, nSize As Long) As Long
#Else
Public Declare Function apiGetUserName Lib "advapi32.dll" Alias _
"GetUserNameA" (ByVal lpBuffer As String, nSize As Long) As Long
#End If
'================================================
Public Function fOSUserName() As String
' Returns the network login name
Dim lngLen As Long, lngX As Long
Dim strUserName As String
strUserName = String$(254, 0)
lngLen = 255
lngX = apiGetUserName(strUserName, lngLen)
If (lngX > 0) Then
fOSUserName = Left$(strUserName, lngLen - 1)
Else
fOSUserName = vbNullString
End If
End Function
Of the 3 methods, the simplest uses the Environ function.
However it is possible to 'spoof' some Environ variables including the user name so this method can not be guaranteed to be accurate. This is the case for both ACCDB & ACCDE files
NOTE:
I am deliberately not going to explain here how this can be done.
As far as I am aware, the other two methods cannot be 'spoofed'.
Therefore, where it is important that the information isn't falsified, use one of methods 2 or 3.
As the WScript method does not need adapting for 32-bit/64-bit systems, that is the approach I would normally recommend.
Click to download an example database:
GetUserName Approx 0.4 MB (zipped)
NOTE:
This is a companion to my GetComputerName article.
Colin Riddington Mendip Data Systems Last Updated 12 Sept 2018